
Control panel systems, often referred to simply as control panels, are integral components of various industrial and commercial systems. They provide a centralized interface for monitoring, controlling, and managing equipment, processes, and operations across diverse industries such as manufacturing, energy and utilities.
Control panels enable increased efficiency and precision in processes, reducing the need for manual labor and human intervention. They also play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and reliability of industrial equipment and allowing for remote monitoring and control.
Here’s a quick run-down on how control panel systems work:
Control panel functionality
Control panels possess a wide range of functionality, depending on the specific application and industry. They may offer capabilities such as:
> Monitoring and displaying real-time data from sensors, meters, and instruments.
> Control of the operation of machinery, equipment, and processes through switches, buttons, and graphical interfaces.
> Implementation of logic and automation using programmable logic controllers (PLCs), relays, and other control devices.
> Provision of alarms, notifications, and alerts for abnormal conditions or events.
> Configuration and adjustment of system parameters and setpoints.
Integration with other systems and devices through communication protocols such as Modbus, Profibus, Ethernet/IP, and DeviceNet.
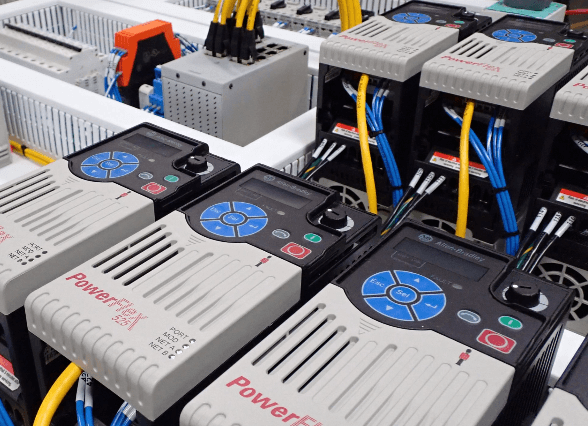
Control panel components
Control panels typically consist of several key components, including:
> A Human-Machine Interface (HMI) displays operational data and allows operators to interact with the system through touchscreens, buttons, and indicators.
> Controllers such as PLCs, microcontrollers, or distributed control systems (DCS) execute control algorithms and logic.
> Power distribution components distribute electrical power to equipment and devices, including circuit breakers, fuses, contactors, and terminal blocks.
> Input/Output (I/O) modules connect sensors, actuators, and other field devices to the control system.
> Communication Interfaces in the form of ports and modules connect the control panel to external devices, networks, and systems.
> Protective enclosures or cabinets house the control panel components, providing physical protection from environmental hazards such as dust, moisture, and temperature extremes.
> Electrical wiring, cables, and connectors interconnect components and devices within the control panel.
Control panel design considerations
Designing control panel systems requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure functionality, reliability, and safety. Key design considerations include:
> Electrical Design: Ensuring compliance with electrical codes and standards, proper sizing of components, and adherence to safety guidelines.
> Environmental Conditions: Selecting appropriate enclosure materials and protection ratings to withstand environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, dust, and corrosive substances.
> Ergonomics: Designing user-friendly interfaces and control layouts for intuitive operation and efficient human-machine interaction.
> Scalability and Expandability: Designing modular and flexible control panel systems that can accommodate future expansions, upgrades, and modifications.
> Maintenance and Serviceability: Incorporating features such as access panels, diagnostic tools, and clear labeling to facilitate maintenance, troubleshooting, and repair.
Control panel applications
Control panel systems find applications across a wide range of industries and sectors, including:
> Industrial Automation Solution: Controlling Automation Solution and monitoring manufacturing processes, machinery, and production lines in industries such as automotive, aerospace, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals.
> Building Automation: Managing HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning), lighting, security, and access control system design in commercial buildings, hospitals, schools, and hotels.
> Energy Management: Monitoring and controlling power generation, distribution, and consumption in utilities, renewable energy systems, and smart grids.
>Transportation: Managing signaling, traffic control, and railway systems in transportation infrastructure such as airports, railways, and highways.
Control panel systems: essential for smart manufacturing and digital transformation
At the core of the manufacturing facility control panel systems play a critical role in optimizing operational control system design efficiency, enhancing safety and ensuring compliance is met across diverse industrial and commercial Automation Solution applications.
Modern and connected control panels combined with effective design, integration, and maintenance of control panel systems are essential for achieving your desired smart manufacturing and digital transformation goals of predictive maintenance and real time, contextualized data on a mobile device.
Struggling with old technology? Don’t know where to start?
AutomateIT’s smart manufacturing consultants are able to meet you where you are at along your journey toward smart factory. Let’s get started!
417.429.4320
[email protected]
What are control panel systems and why are they critical pieces of plant infrastructure?

Control panel systems, often referred to simply as control panels, are integral components of various industrial and commercial systems. They provide a centralized interface for monitoring, controlling, and managing equipment, processes, and operations across diverse industries such as manufacturing, energy and utilities.
Control panels enable increased efficiency and precision in processes, reducing the need for manual labor and human intervention. They also play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and reliability of industrial equipment and allowing for remote monitoring and control.
Here’s a quick run-down on how control panel systems work:
Control panel functionality
Control panels possess a wide range of functionality, depending on the specific application and industry. They may offer capabilities such as:
> Monitoring and displaying real-time data from sensors, meters, and instruments.
> Control of the operation of machinery, equipment, and processes through switches, buttons, and graphical interfaces.
> Implementation of logic and automation using programmable logic controllers (PLCs), relays, and other control devices.
> Provision of alarms, notifications, and alerts for abnormal conditions or events.
> Configuration and adjustment of system parameters and setpoints.
Integration with other systems and devices through communication protocols such as Modbus, Profibus, Ethernet/IP, and DeviceNet.

Control panel components
Control panels typically consist of several key components, including:
> A Human-Machine Interface (HMI) displays operational data and allows operators to interact with the system through touchscreens, buttons, and indicators.
> Controllers such as PLCs, microcontrollers, or distributed control systems (DCS) execute control algorithms and logic.
> Power distribution components distribute electrical power to equipment and devices, including circuit breakers, fuses, contactors, and terminal blocks.
> Input/Output (I/O) modules connect sensors, actuators, and other field devices to the control system.
> Communication Interfaces in the form of ports and modules connect the control panel to external devices, networks, and systems.
> Protective enclosures or cabinets house the control panel components, providing physical protection from environmental hazards such as dust, moisture, and temperature extremes.
> Electrical wiring, cables, and connectors interconnect components and devices within the control panel.
Control panel design considerations
Designing control panel systems requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure functionality, reliability, and safety. Key design considerations include:
> Electrical Design: Ensuring compliance with electrical codes and standards, proper sizing of components, and adherence to safety guidelines.
> Environmental Conditions: Selecting appropriate enclosure materials and protection ratings to withstand environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, dust, and corrosive substances.
> Ergonomics: Designing user-friendly interfaces and control layouts for intuitive Control panel systems operation and efficient human-machine interaction.
> Scalability and Expandability: Designing modular and flexible control panel systems that can accommodate future expansions, upgrades, and modifications.
> Maintenance and Serviceability: Incorporating features such as access panels, diagnostic tools, and clear labeling to facilitate maintenance, troubleshooting, and repair.
Control panel applications
Control panel systems find applications across a wide range of industries and sectors, including:
> Industrial Automation Solution: Controlling and monitoring manufacturing processes, Automation Solution machinery, and production lines in industries such as automotive, aerospace, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals.
> Building Automation: Managing HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning), lighting, security, and access control system design in commercial buildings, hospitals, schools, and hotels.
> Energy Management: Monitoring and controlling power generation, distribution, and consumption in utilities, renewable energy systems, and smart grids.
>Transportation: Managing signaling, traffic control, and railway systems in transportation infrastructure such as airports, railways, and highways.
Control panel systems: essential for smart manufacturing and digital transformation
At the smart manufacturing core of the manufacturing facility control panel systems play a critical role in optimizing operational efficiency, enhancing safety and ensuring compliance is met across diverse industrial and commercial applications.
Modern and connected control panels combined with effective design, integration, and maintenance of control panel systems are essential for achieving your desired smart manufacturing and digital transformation goals of predictive maintenance and real time, contextualized data on a mobile device.
Struggling with old technology? Don’t know where to start?
AutomateIT’s smart manufacturing consultants are able to meet you where you are at along your journey toward smart factory. Let’s get started!
417.429.4320
[email protected]
What are control panel systems and why are they critical pieces of plant infrastructure?

Control panel systems, often referred to simply as control panels, are integral components of various industrial and commercial systems. They provide a centralized interface for monitoring, controlling, and managing equipment, processes, and operations across diverse industries such as manufacturing, energy and utilities.
Control panels enable increased efficiency and precision in processes, reducing the need for manual labor and human intervention. They also play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and reliability of industrial equipment and allowing for remote monitoring and control.
Here’s a quick run-down on how control panel systems work:
Control panel functionality
Control panels possess a wide range of functionality, depending on the specific application and industry. They may offer capabilities such as:
> Monitoring and displaying real-time data from sensors, meters, and instruments.
> Control of the operation of machinery, equipment, and processes through switches, buttons, and graphical interfaces.
> Implementation of logic and automation using programmable logic controllers (PLCs), relays, and other control devices.
> Provision of alarms, notifications, and alerts for abnormal conditions or events.
> Configuration and adjustment of system parameters and setpoints.
Integration with other systems and devices through communication protocols such as Modbus, Profibus, Ethernet/IP, and DeviceNet.

Control panel components
Control panels typically consist of several key components, including:
> A Human-Machine Interface (HMI) displays operational data and allows operators to interact with the system through touchscreens, buttons, and indicators.
> Controllers such as PLCs, microcontrollers, or distributed control systems (DCS) execute control algorithms and logic.
> Power distribution components distribute electrical power to equipment and devices, including circuit breakers, fuses, contactors, and terminal blocks.
> Input/Output (I/O) modules connect sensors, actuators, and other field devices to the control system.
> Communication Interfaces in the form of ports and modules connect the control panel to external devices, networks, and systems.
> Protective enclosures or cabinets house the control panel components, providing physical protection from environmental hazards such as dust, moisture, and temperature extremes.
> Electrical wiring, cables, and connectors interconnect components and devices within the control panel.
Control panel design considerations
Designing control panel systems requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure functionality, reliability, and safety. Key design considerations include:
> Electrical Design: Ensuring compliance with electrical codes and standards, proper sizing of components, and adherence to safety guidelines.
> Environmental Conditions: Selecting appropriate enclosure materials and protection ratings to withstand environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, dust, and corrosive substances.
> Ergonomics: Designing user-friendly interfaces and control layouts for intuitive operation and efficient human-machine interaction.
> Scalability and Expandability: Designing modular and flexible control panel systems that can accommodate future expansions, upgrades, and modifications.
> Maintenance and Serviceability: Incorporating features such as access panels, diagnostic tools, and clear labeling to facilitate maintenance, troubleshooting, and repair.
Control panel applications
Control panel systems find applications across a wide range of industries and sectors, including:
> Industrial Automation Solution: Controlling and monitoring manufacturing processes, machinery, and production lines in industries such as automotive, aerospace, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals.
> Building Automation: Managing HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning), lighting, security, and access control system design in commercial buildings, hospitals, schools, and hotels.
> Energy Management: Monitoring and controlling power generation, distribution, and consumption in utilities, renewable energy systems, and smart grids.
>Transportation: Managing signaling, traffic control, and railway systems in transportation infrastructure such as airports, railways, and highways.
Control panel systems: essential for smart manufacturing and digital transformation
At the core of the manufacturing facility control panel systems play a critical role in optimizing operational efficiency, enhancing safety and ensuring compliance is met across Control panel systems diverse industrial and commercial applications.
Modern and connected control panels combined with effective design, integration, and maintenance of control panel systems are essential for achieving your desired smart manufacturing and digital transformation goals of predictive maintenance and real time, contextualized data on a mobile device.
Struggling with old technology? Don’t know where to start?
AutomateIT’s smart manufacturing consultants are able to meet you where you are at along your journey toward smart factory. Let’s get started!
417.429.4320
[email protected]
What are control panel systems and why are they critical pieces of plant infrastructure?

Control panel systems, often referred to simply as control panels, are integral components of various industrial and commercial systems. They provide a centralized interface for monitoring, controlling, and managing equipment, processes, and operations across diverse industries such as manufacturing, energy and utilities.
Control panels enable increased efficiency and precision in processes, reducing the need for manual labor and human intervention. They also play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and reliability of industrial equipment and allowing for remote monitoring and control.
Here’s a quick run-down on how control panel systems work:
Control panel functionality
Control panels possess a wide range of functionality, depending on the specific application and industry. They may offer capabilities such as:
> Monitoring and displaying real-time data from sensors, meters, and instruments.
> Control of the operation of machinery, equipment, and processes through switches, buttons, and graphical interfaces.
> Implementation of logic and automation using programmable logic controllers (PLCs), relays, and other control devices.
> Provision of alarms, notifications, and alerts for abnormal conditions or events.
> Configuration and adjustment of system parameters and setpoints.
Integration with other systems and devices through communication protocols such as Modbus, Profibus, Ethernet/IP, and DeviceNet.

Control panel components
Control panels typically consist of several key components, including:
> A Human-Machine Interface (HMI) displays operational data and allows operators to interact with the system through touchscreens, buttons, and indicators.
> Controllers such as PLCs, microcontrollers, or distributed control systems (DCS) execute control algorithms and logic.
> Power distribution components distribute electrical power to equipment and devices, including circuit breakers, fuses, contactors, and terminal blocks.
> Input/Output (I/O) modules connect sensors, actuators, and other field devices to the control system.
> Communication Interfaces in the form of ports and modules connect the Automation Solution control panel to external devices, networks, and systems.
> Protective enclosures or cabinets house the control panel components, providing physical protection from environmental hazards such as dust, moisture, and temperature extremes.
> Electrical wiring, cables, and connectors interconnect components and devices within the control panel.
Control panel design considerations
Designing control panel systems requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure functionality, reliability, and safety. Key design considerations include:
> Electrical Design: Ensuring compliance with electrical codes and smart manufacturing standards, proper sizing of components, and adherence to safety guidelines.
> Environmental Conditions: smart manufacturing Selecting appropriate enclosure materials and protection ratings to withstand environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, dust, and corrosive substances.
> Ergonomics: Designing user-friendly interfaces and control layouts for intuitive operation and efficient human-machine interaction.
> Scalability and Expandability: Designing modular and flexible control panel systems that can accommodate future expansions, upgrades, and modifications.
> Maintenance and Serviceability: Incorporating features such as access panels, diagnostic tools, and clear labeling to facilitate maintenance, troubleshooting, and repair.
Control panel applications
Control panel systems find applications across a wide range of industries and sectors, including:
> Industrial Automation Solution: Controlling and monitoring manufacturing processes, machinery, and production lines in industries such as automotive, aerospace, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals.
> Building Automation: Managing HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning), lighting, security, and access control system design in commercial buildings, hospitals, schools, and hotels.
> Energy Management: Monitoring and controlling power generation, distribution, and consumption in utilities, renewable energy systems, and smart grids.
>Transportation: Managing signaling, traffic control, and railway systems in transportation infrastructure such as airports, railways, and highways.
Control panel systems: essential for smart manufacturing and digital transformation
At the core of the manufacturing facility control panel systems play a critical role in optimizing operational efficiency, enhancing safety and ensuring compliance is met across diverse industrial and commercial applications.
Modern and connected control panels combined with effective design, integration, and maintenance of control panel systems are essential for achieving your desired smart manufacturing and digital transformation goals of predictive maintenance and real time, contextualized data on a mobile device.
Struggling with old technology? Don’t know where to start?
AutomateIT’s smart manufacturing consultants are able to meet you where you are at along your journey toward smart factory. Let’s get started!
417.429.4320
[email protected]
What are control panel systems and why are they critical pieces of plant infrastructure?

Control panel systems, often referred to simply as control panels, are integral components of various industrial and commercial systems. They provide a centralized interface for monitoring, controlling, and managing equipment, processes, and operations across diverse industries such as manufacturing, energy and utilities.
Control panels enable increased efficiency and precision in processes, reducing the need for manual labor and human intervention. They also play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and reliability of industrial equipment and allowing for remote monitoring and control.
Here’s a quick run-down on how control panel systems work:
Control panel functionality
Control panels possess a wide range of functionality, depending on the specific application and industry. They may offer capabilities such as:
> Monitoring and displaying real-time data from sensors, meters, and instruments.
> Control of the operation of machinery, equipment, and processes through switches, buttons, and graphical interfaces.
> Implementation of logic and automation using programmable logic controllers (PLCs), relays, and other control devices.
> Provision of alarms, notifications, and alerts for abnormal conditions or events.
> Configuration and adjustment of system parameters and setpoints.
Integration with other systems and devices through communication protocols such as Modbus, Profibus, Ethernet/IP, and DeviceNet.

Control panel components
Control panels typically consist of several key components, including:
> A Human-Machine Interface (HMI) displays operational data and allows operators to interact with the system through touchscreens, buttons, and indicators.
> Controllers such as PLCs, microcontrollers, or distributed control systems (DCS) execute control algorithms and logic.
> Power distribution components distribute electrical power to equipment and devices, including circuit breakers, fuses, contactors, and terminal blocks.
> Input/Output (I/O) modules connect sensors, actuators, and other field devices to the control system.
> Communication Interfaces in the form of ports and modules connect the control panel to external devices, networks, and systems.
> Protective enclosures or cabinets house the control panel components, providing physical protection from environmental hazards such as dust, moisture, and temperature extremes.
> Electrical wiring, cables, and connectors interconnect components and devices within the control panel.
Control panel design considerations
Designing control panel systems requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure functionality, reliability, and safety. Key design considerations include:
> Electrical Design: Ensuring smart manufacturing compliance with electrical codes and standards, smart manufacturing proper sizing of components, and adherence to safety guidelines.
> Environmental Conditions: Selecting appropriate enclosure materials and protection ratings to withstand environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, dust, and corrosive substances.
> Ergonomics: Designing user-friendly interfaces and control layouts for intuitive operation and efficient human-machine interaction.
> Scalability and Expandability: Designing modular and flexible control panel systems that can accommodate future expansions, upgrades, and modifications.
> Maintenance and Serviceability: Incorporating features such as access panels, diagnostic tools, and clear labeling to facilitate maintenance, troubleshooting, and repair.
Control panel applications
Control panel systems find applications across a wide range of industries and sectors, including:
> Industrial Automation Solution: Controlling and monitoring manufacturing processes, machinery, and production lines in industries such as automotive, aerospace, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals.
> Building Automation: Managing HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning), lighting, security, and access control system design in commercial buildings, hospitals, schools, and hotels.
> Energy Management: Monitoring and controlling power generation, distribution, and consumption in utilities, renewable energy systems, and smart grids.
>Transportation: Managing signaling, traffic control, and railway systems in transportation infrastructure such as airports, railways, and highways.
Control panel systems: essential for smart manufacturing and digital transformation
At the core of the manufacturing facility control panel systems play a critical role in optimizing operational efficiency, enhancing safety and ensuring compliance is met across diverse industrial and commercial applications.
Modern and connected control panels combined with effective design, integration, and maintenance of control panel systems are essential for achieving your desired smart manufacturing and digital transformation goals of predictive maintenance and real time, contextualized data on a mobile device.
Struggling with old technology? Don’t know where to start?
AutomateIT’s smart manufacturing consultants are able to meet you where you are at along your smart manufacturing journey toward smart factory. Let’s get started!
417.429.4320
[email protected]